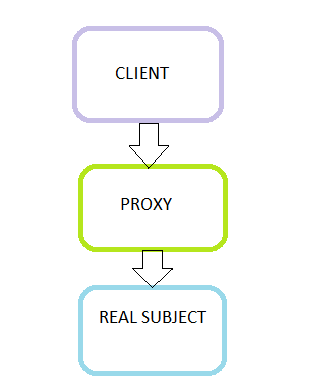
Proxy Design Pattern
“Provide a surrogate or placeholder for another object to control access to it” is the intent provided by GoF.
Proxy means ‘in place of’. In attendance roll call, we give proxy for our friends in college right? ‘Representing’ or ‘in place of’ or ‘on behalf of’ are literal meanings of proxy and that directly explains proxy design pattern. It is one of the simplest and straight forward design pattern.
Proxy design pattern gets second rank in popularity in interviews. Guess who gets the first rank? none other than singleton design pattern.
Possible Usage Scenarios
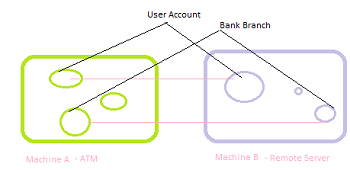
- Remote Proxy – Represents an object locally which belongs to a different address space. Think of an ATM implementation, it will hold proxy objects for bank information that exists in the remote server. RMI is an example of proxy implmenetation for this type in java.
- Virtual Proxy – In place of a complex or heavy object use a skeleton representation. When an underlying image is huge in size, just represent it using a virtual proxy object and on demand load the real object. You feel that the real object is expensive in terms of instantiation and so without the real need we are not going to use the real object. Until the need arises we will use the virtual proxy.
- Protection Proxy – Are you working on a MNC? If so, you might be well aware of the proxy server that provides you internet. Saying more than provides, the right word is censores internet. The management feels its better to censor some content and provide only work related web pages. Proxy server does that job. This is a type of proxy design pattern. Lighter part of censor is, we search for something critical in Google and click the result and you get this page is blocked by proxy server. You never know why this page is blocked and you feel this is genuine. How do you overcome that, over a period you learn to live with it.
- Smart Reference – Just we keep a link/reference to the real object a kind of pointer.
Proxy Design Pattern Example
Remote Proxy:
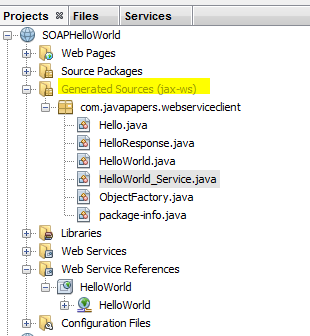
Sometime back I wrote an article on A helloworld for Soap Web Service. A part of it contains implementation of proxy design pattern. The client has the stub files generated which acts as a proxy for the classes in server side.
Java’s Support for Proxy Design Pattern
From JDK 1.3 java has direct support for implementing proxy design pattern. We need not worry on mainting the reference and object creation. Java provides us the needed utilities. Following example implementation explains on how to use java’s api for proxy design pattern.
package com.javapapers.designpattern.proxy;
public interface Animal {
public void getSound();
}
package com.javapapers.designpattern.proxy;
public class Lion implements Animal {
public void getSound() {
System.out.println("Roar");
}
}
package com.javapapers.designpattern.proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class AnimalInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
public AnimalInvocationHandler(Object realSubject) {
this.realSubject = realSubject;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method m, Object[] args) {
Object result = null;
try {
result = m.invoke(realSubject, args);
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
private Object realSubject = null;
}
package com.javapapers.designpattern.proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class ProxyExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal realSubject = new Lion();
Animal proxy = (Animal) Proxy.newProxyInstance(realSubject.getClass()
.getClassLoader(), realSubject.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new AnimalInvocationHandler(realSubject));
proxy.getSound();
}
}
Download Proxy Example Source
Important Points
- A proxy may hide information about the real object to the client.
- A proxy may perform optimization like on demand loading.
- A proxy may do additional house-keeping job like audit tasks.
- Proxy design pattern is also known as surrogate design pattern.
Proxy Design Pattern Usage in Java API
- java.rmi.* – RMI package is based on proxy design pattern
Adapter vs Proxy Design Pattern
Adapter design pattern provides a different interface from the real object and enables the client to use it to interact with the real object. But, proxy design pattern provides the same interface as in the real object.
Decorator vs Proxy Design Patter
Decorator design pattern adds behaviour at runtime to the real object. But, Proxy does not change the behaviour instead it controls the behaviour.
Comments on "Proxy Design Pattern"
Comments are closed for "Proxy Design Pattern".



Really useful bolg for java developers.
Your are simple and superb ……
Really very helpful for me ,Can you post Java Refrences like weak refrences,soft refrences,Strong refrences,phenotne refrences
Can you make it simple for me i tried hard and there are blog but cant satisfy…
Thanx….
Great Explanation!!
Great Explanation Joe, this blog is Very very help ful to me…..,
Thanks, but this is not a proxy. This is a dynamic proxy.
its really appreciating thing , bcz of very useful for beginners like me
Simple explanation …. good sir.
Hi Joe,
Could you please consider adding one heading “Prototype vs Proxy Design Pattern” at the end of this article?
Thanks,
Amitabha
Good one
HI Joe,
What happened no updates from the last 20days. your site is very awesome. i am adaily follower of u r site
Hi Joe
Could you please provide some insight regarding performance issues in Java.
May God Bless you!!
Thanks in Advance.
Regards
Prasad Varikuti
Good one
Wonderful !!
THis is what I was trying to understand !
Great article man!!
Thank you, lot of complicated topics expressed in simple and understandable terms. Thanks again.
Nice Article
the easiest and most logical examples on design patterns… suprisingly how much we use without knowing theyre actually design patterns…
amazing, thanks…
Awesome…..
Just superb.. nice example
you are my proxy :)
the best explanation of Design patters. thanks so much for the help
very very neat and good …. ! thankyou….
Very good example
really usefull
Good one. Very informative
Keep Posting!
Regards,
Amir Iqbal
This web site is really very good and it gives you understanding of concepts that you will never forget.
Hi joe,
You are the man!!!
Simple and superb!
very nice
Nice article
Very Informative.
I have read many java and design pattern related articles from your blog.
Articles on your blog are very good and very simple.
Thanks for all this great work !!
Excellent blog
Very Nice article…enjoyed reading it ! and examples are lively !!!! good choice of words !!!!!
Very good illustration. Thank you.
Sorry but I was not able to understand it fully :(
vv
simply super boss
very good…
Really informative post .
Composite design pattern is based on creating a tree structure in such a way that an individual leaf of the tree can be treated just like entire tree composition.
I have one question regarding the proxy creation. The issue is we are doing
// creating the real object
Animal realSubject = new Lion();
// creating the proxy object using the real object
Animal proxy = (Animal) Proxy.newProxyInstance(realSubject.getClass()
.getClassLoader(), realSubject.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new AnimalInvocationHandler(realSubject));
So my question is how it is different from calling the method directly by realSubject.getSound();, I mean to say how we are getting benefit by creating the proxy as proxy seems to be a very lightweight object? Also if you see the hashcode of proxy object and realSubject, both of them are giving same hashcode.