Dependency Injection (DI) with Spring
In this tutorial we will learn about what is dependency injection (DI) and how Spring framework supports DI. Couple of weeks back we saw a tutorial on Spring MVC and this is a continuation in this series.
Table of Contents
- Dependency Injection
- Difference between Dependency Injection and Factory
- Advantages of Dependency Injection
- Dependency Injection Types
- Spring DI
- Spring Dependency Injection using Annotations
- Spring Dependency Injection using XML
- Download Spring IOC Example Source Code
1. Dependency Injection
Dependency injection is a jargon created by Martin Fowler and it is also called as inversion of control. In object oriented design, objects have relationship with one another. A class (A) can have attributes (B) and methods. Those attributes are again instances of another class (C). If class (A) wants to work and perform its objective, attributes (B) should be instantiated.
There are different ways to instantiate an object and we have seen a lot in our design pattern tutorial series. A simple and direct way is to use the “new” operator and call the constructor of Class (C) where we need that instance in class (A). This is class A has obsolute control over creation of attribute (B). It decides which class (C) to call and how to call etc.

Now, if we outsource that ‘instantiation and supplying an instance’ job to some third party. Class (A) needs instance of class (C) to operate, but it outsources that responsibility to some third party. The designated third party, decides the moment of creation and the type to use to create the instance. The dependency between class (A) and class (C) is injected by a third party. Whole of this agreement involves some configuration information too. This whole process is called dependency injection.

2. Difference between Dependency Injection and Factory
Factory design pattern and dependency injection may look related but we look at them with microscope then we can understand the are different. Even if we use a factory the dependent class has the responsibility of creating the instance but the core of dependency injection is separating that responsibility to external component.
2.1 Factory Example:
Class A {
private C obj;
public void someMethod() {
...
this.obj = MyObjectFactory.getC();
...
}
}
2.2 With Dependency Injection:
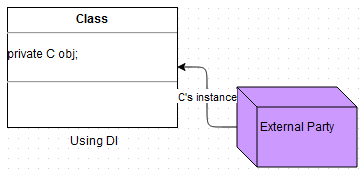
Class A {
private C obj;
public void someMethod(C obj) {
...
this.obj = obj;
...
}
}
With DI the contract is different, pass C’s instance to get the job done. So the responsibility is with an external person to decide.
3. Advantages of Dependency Injection
- Loosely couple architecture.
- Separation of responsibility
- Configuration and code is separate.
- Using configuration, a different implementation can be supplied without changing the dependent code.
- Testing can be performed using mock objects.
4. Dependency Injection Types
Dependency injection is classified into three categories namely,
- Constructor Injection
- Setter Injection
- Interface-based Injection
Definition for the above are explicit. When the dependency is solved using constructor it is called constructor injection :-) That is, the dependent object is passed as a parameter in the dependent class’s constructor. Similarly for setter injection, the instance is injected using a setter method. In interface-based dependency injection, we will have an interface and on implementing it we will get the instance injected.
5. Spring DI
Spring framework provides many modules and its core has an inversion of control (IOC) container. Spring’s IOC container is light-weight and it manages the dependency between objects using configurations. It wires the related objects together, instantiates and supplies them based on configuration. In Spring, these objects are called managed objects. Spring and dependency injection is a large area and requires multiple articles to get an indepth idea. In this tutorial, my intent is to give an introduction and subsequently write more articles on it.
Two most popular ways in Spring for DI is, constructor and setter injection. Configuration for dependency are done using Spring-configuration XML or using annotations. Annotations are mostly preferred for their ease of use. Spring manages these objects using BeanFactory. When an instance is created, by default they are singletons and this can be changed using the configuration.
5.1 Circular Dependency
What is circular dependency and tell about it is a popular question in Spring interviews. A -> B -> A, A is dependent on B and vice-versa. Spring’s IOC container will detect such circular dependencies at runtime and throws ObjectCurrentlyInCreationException. This is more prevalent in the case of constructor injection.
6. Spring Dependency Injection using Annotations
WildAnimal.java – Interface backbone using which dependency injection is done.
package com.javapapers.spring.ioc;
public interface WildAnimal {
public String sound() ;
}
Lion.java – Implements the above interface and becomes a possible candidate for injection.
package com.javapapers.spring.ioc;
public class Lion implements WildAnimal {
public String sound() {
return "Roar";
}
}
Wolf.java – another implementation of interface. This is the selected implementation for injection. @Service tells the spring IOC container to use this class.
package com.javapapers.spring.ioc;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class Wolf implements WildAnimal {
public String sound() {
return "Howl";
}
}
Zoo.java – Zoo depends on WildAnimal and uses setter injection. @Autowired tells the Spring IOC container to find configured object of this type and inject an instance at runtime.
package com.javapapers.spring.ioc;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class Zoo {
private WildAnimal wild;
@Autowired
public void setWild(WildAnimal wild) {
this.wild = wild;
}
public void testSound() {
System.out.println(wild.sound());
}
}
spring-context.xml – gives the configuration information to the spring container. In this I describe that we are using annotation based configurations.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<!-- Dependency Injection with annotations -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.javapapers.spring.ioc" />
<mvc:annotation-driven />
<!-- Dependency Injection without annotations -->
<!--
<bean id="wild" class="com.javapapers.spring.ioc.Wolf" />
<bean id="zoo" class="com.javapapers.spring.ioc.Zoo">
<property name="wild" ref="wild" />
</bean>
-->
</beans>
TestDI.java – loads the spring configuration and gets the bean. Spring IOC container based on annotations, provides the Wolf.java instance at runtime.
package com.javapapers.spring.ioc;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestDI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext appContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("META-INF/spring-context.xml");
BeanFactory factory = appContext;
Zoo zoo = (Zoo) factory.getBean("zoo");
zoo.testSound();
}
}
7. Spring Dependency Injection using XML
We can remove all the annotations in the java classes. In spring configuration we declare the chosen implementation to supply at runtime.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<!-- Dependency Injection with annotations -->
<!-- <context:component-scan base-package="com.javapapers.spring.ioc" />
<mvc:annotation-driven /> -->
<!-- Dependency Injection without annotations -->
<bean id="wild" class="com.javapapers.spring.ioc.Wolf" />
<bean id="zoo" class="com.javapapers.spring.ioc.Zoo">
<property name="wild" ref="wild" />
</bean>
</beans>
8. Download Spring IOC Example Source Code
Comments on "Dependency Injection (DI) with Spring"
Comments are closed for "Dependency Injection (DI) with Spring".



nice collections
Very nice tutorial, respect to author.
nice tutorial……………
very nice example to explain DI…
Thanks Joe,
Expecting more in up coming Spring concepts
Expecting more in spring concepts.Nice Explain.
Thanks Joe,
good one sir :)
Your wording is so much clear and perfect. Articles are easy to understand.. Hoping to see lot more topics to cover from Spring.
Yah this material is helping me alot .
dep-inj topic is very good and i am also expecting more concepts from Spring
Nice one sir, with easy presentation. I hope u vl cover or update concepts of STRUTS also. If u provide STRUTS also it will be very helpful. Thanks..
Very nice explanation.. Expecting more from you about spring with database connection with example.. Hope you will conver lot about spring in your next article.
Hots of your excellent work.
Thanks Joe sir,
Its a very nice tutorial to learn and understand spring.
Simple and easy understand. Thanks Joe!
One Word. BRILLIANT! An explanation given in such a neat and simple way that makes the concept so clear. Great work, Keep it flowing!
Looking forward for articles on Hibernate as well :)
explanation given in such simple way that makes the concept so clear.
Good one.
Great one, Joe ! Thanks much.
Good
Very Nice Explanation, makes feel to understand so simple ! Thank You
i cant live without Spring nowadays. It’a a must when coding java web projects
Great article,Many thanks sir..
Great helping source sir..
Look forward more spring hibernate tutorials
its very useful thank u
Nice tutorial , easy to understand for the beginners and explained with the clarity.
gud
Nice tutorial….can u provide this explanation with small demonstration……..
I didn’t get much info regarding the difference between Annotation based & XML based DI. Is it the only difference is commenting ”
??
How i can create zoo with lion / wolf at runtime interchangeble?
Its a nice tutorial..
ooosm tutorial for DI intro.
hii joe ,
can u plz show hot to do this program using xml configurations instead of annotations…
Hi, I don’t want to use anything in my Spring XML. And in my web application, how do I achieve DI. Is there a way to achieve it only by using Annotations? Something similar to @Inject in JavaEE 6 standards..is there a way to achieve it?
I mean, I dont want to have this piece of code,
ApplicationContext appContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“META-INF/spring-context.xml”);
BeanFactory factory = appContext;
Zoo zoo = (Zoo) factory.getBean(“zoo”);
Great tutorial using simplest language…
Good job Sir jee…
thank you sir.
sir ur explanation is super on dependency injection.
sir, i want spring acegi security means authentication and autherization concepts with small example.
please tell me sir…
Really very good explanation for DI.. Thank you Joe.
VERY VERY NICE EXPL
Using
Zoo zoo = (Zoo) factory.getBean(“zoo”);
Is not a dependency Injection. I found in some articles found in the internet. Would you agree?
Yes this is not dependency injection.
can you please post constructor based dependency injection too and how to pass a dbobject in constructor
the same example is exist in many sites…post some other example….
Nice tutorial. .thanx. .
very usefull
very useful sir
Very Good and Helpfull
Easy to Understand and the examples are quite self explanatory.
Thanks a lot!
Good work………….
THANK YOU!! I have spent the entire afternoon trying to understand DI, but I was still so confused. I finally got it after reading your little tutorial.
Thanks Joe, you explained well… I have downloaded this source code but unbale to run it because of jars.. could you please let me know about required jars to execute it. Many Thanks in Advance.
good one thanks…………………
Thanks for the Post Joe.. But I cant able to understand where DI working in this example….Could you pls explain
Very Nice and concise tutorial. Thanks.
Hi ,
I am new to spring framework.I think in above example, you should define bean in application context xml file whether it’s autowired or xml based configuration .
but in source code you have written,
<!–
–>
why you commented all beans if you are configuring using annotation??
Please reply me i am new to this framework.
Thanks a lot joy.for such a useful and easily understandable material..each time i am reading your block and getting more and more knowledge…
Thank you Joe ! Simple and good explanation , that is your way .
Very nice explanation.. Expecting more from you about spring
Nice one.
It’s the best, srsly! :)
Hi, I got an error while eaxecute the above code.
Error occurred during initialization of VM
java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError: java.lang.Class.desiredAssertionStatus0(Ljava/lang/Class;)Z
<> “
Hi
I have one confusion if I have interface which is implements by class A and I have some method in that class A but by using dependency injection i want to use those method in class B how I can do it Please clear this doubt.
thanks in advance
easy to understand
easy to understand
Gud One!!!! Very helpful!!! Thanks…
nice tutorial
nice collections very useful for us, please provide struts materials also, it will be more useful to us
Regards
anitha
awesom
Awesom…….. :)
Thanks for the nice article. Could you please explain the elegant way of coding if Lion is also annotated as service and at run time dynamically need to inject either Lion or wolf?
Tell me how to resolve circular dependancy?
thank a lot , very easy to understand tutorial
thank a lot , nice tutorial
It is very nice article.
I have few questions to ask on Circular dependency?
How the spring container detects that there is a circular dependency exists between classes?
Could you please provide me an example where circular dependency exists?
Why
Zoo zoo = (Zoo) factory.getBean(“zoo”); this is not dependency injection.
Many people saying interface injection is not possible in spring ,can you tell me why and what is exactly interface injection?
Very nice explanation.. Thank you.
Hi joe,
can you please explain the benefits of dependency injection in detail?
Hi Joe,
It is good informative and understandable. you have explained very well. “DON’T CALL ME, I’LL CALL YOU” This one sentence enough to understand the concept of Dependency Injection. I expecting more on spring from you.
Hi Joe,
I got this interview question in one of the interviews.
Is IOC possible with DI?
I answered Yes.
DI is Injecting Dependancies.
Since the process of DI is managed by the container and not us , the flow is reversed hence it is Inversion Of Control.
So ideally, The Servlet which instantiated by container, whose lifecyle methods are managed by the web container, is also IOC? but not DI?
Am I correct? Please explain.
Regards,
-Pankaj.
Hi joe, Nice article
I have a question, can you explain these line clearly?
” it manages the dependency between objects using configurations. It wires the related objects together, instantiates and supplies them based on configuration. In Spring, these objects are called managed objects”
What is this wiring? and wiring together?
Dear Joe,
Please explain how spring internally make singletone
Does it make private constructor , then static instance variable
And check in if else condition.Please help about the internal implementation of
Singleton and prototype.
Tahnks
Abhishek
Thanks a lot for this..
Dear Joe,
I am new to Spring, and currently I am working on Flex project which uses Spring WebMVC framework. I am unable to understand one thing, I have a jar in my lib folder which uses a config.xml file having a Spring factory defined. Now I am having a doubt as to how I can use this SpringFactory id in my config.xml file so that there will be two factories which will be configured.
Thanks in advance.
It’s good thanks for the sharing information
I’ve been looking for a clear explanation of this topic for awhile now and couldn’t find one. Thanks actually explaining Spring clearly.
Hi Joe,
I would like to know if we can run a spring application without activating either of the spring containers(Bean Factory and Application Context). I am working on a spring web application where i didn’t see any activation of the above mentioned containers in java code. Your answer would be much appreciated.
Thanks,
Sriharsha K
Nice article for beginners to understand the spring concepts.
Thanks for your spring materials. And one more request (from everyone) could you please add information about MAVEN. Coz that really help us to work with better understanding.
Like * Purpose
* Use
* Advantages
* How to work with
Thanks in advance.
Cyril