Servlet Getting Started
This part of the servlet tutorial is to setup the development environment required to execute Servlets.
Install and Setup Java
To run the Java Servlets we need a Servlet container like Apache Tomcat. Before going into detail of installing the servlet container we need to install Java and it is a prerequisite.
Download the latest version of JDK from Oracle download center. And install it. If the OS is Windows then the install is fairly straight forward, click next next next and finish. If it is Linux based distributions, believe me it is easier than that. Just a simple command will do. So once installation is done, set the JAVA_HOME variable,
set JAVA_HOME="C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0"
The GUI may be used to set the environment variable permanently. Go to ‘advanced system settings’ – > system properties –> advanced –> Environment Variables
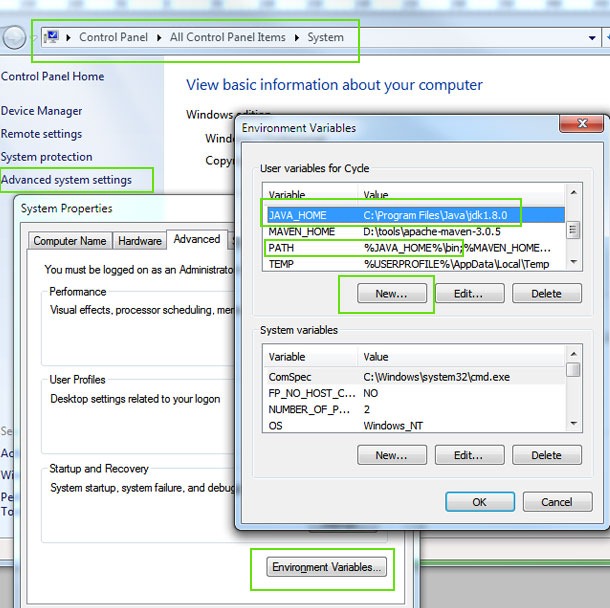
If its Linux based,
setenv JAVA_HOME /usr/local/jdk1.8.0
Additionally you may also set the Java classpath
Install and Setup Apache Tomcat
Apache tomcat is the popular servlet container. It is simple, easy and powerful. Download the setup exe from the Apache site and as usual next next next.
Once the Apache Tomcat is installed as similar to JAVA_HOME, add a system variable as CATALINA_HOME for the home installation directory of Apache Tomcat.
set CATALINA_HOME="C:\Program Files\Apache Software Foundation\Tomcat 7.0"
Start / Stop Tomcat
In windows there will be an utility named “Monitor Tomcat” installed along with Apache Tomcat installation. It can be used to start and stop tomcat.
Start the Tomcat and go the URL http://localhost:8080/ in a web browser. A page similar to the following screen shot should be shown based on the version of Tomcat installed.
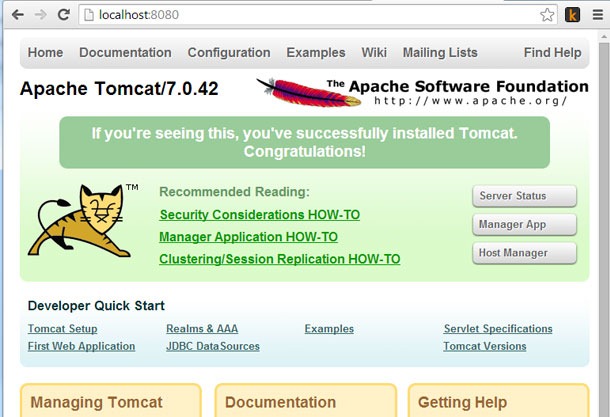
In Linux startup.sh and shutdown.sh scripts can be used to start and stop it.
Servlet API Classpath
To do development using Java servlets, Servlet API implementation is needed. In Tomcat installation lib folder, in my case “C:\Program Files\Apache Software Foundation\Tomcat 7.0\lib” a Jar file named servlet-api.jar can be found. It should be added to the CLASSPATH to develop using Servlets. There are many ways to add this Jar to the classpath. This can be bundled along with the application itself or else it can be added to the system classpath as given in this linked Java classpath tutorial.
Comments on "Servlet Getting Started"
Comments are closed for "Servlet Getting Started".



Short and simple as always.
Effective enough :)